Polar vs Non-Polar Covalent Bonds & Molecules
A polar bond is a covalent bond in which the electrons that form the bond are inequally distributed between two atoms. While a non-polar bond is a covalent bond in which electrons that form the bond are equally distributed between two atoms. Electronegativity determines whether a bond is polar or non-polar.
The tendency of an atom or a functional group to attract electrons toward itself is known as Electronegativity.
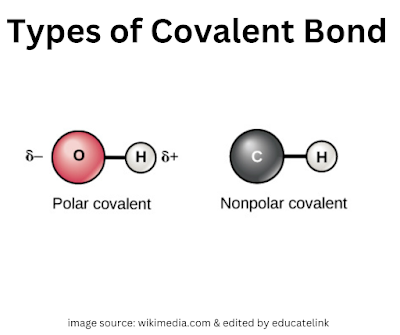 |
Polar bond and non-polar bond |
Polar covalent bond
- Electrons spend more time on one side of the bond in a polar bond.
- They are intermediate between ionic bonds and pure covalent bonds.
- A polar covalent bond is formed when the electronegativity differences of cation and anion are between 0.4 and 1.7.
- They are formed between two nonmetal atoms that have different electronegativity.
- There is a dipole moment between the atoms.
Non-polar covalent bond
- In non-polar bonds, the difference in electronegativity is mostly negligible.
- They are formed between two nonmetal atoms that have identical electronegativity.
- There is no dipole moment between the atoms.
- When atoms that share a polar bond arrange themselves in such a way that electric charges tend to cancel each other out, a Non-polar covalent bond can be formed.
Difference between Polar and Non-polar covalent bonds (Polar vs Non-polar)
|
Properties |
Polar |
Non-polar |
Physical State |
Polar
covalent compounds can exist in solid forms because of the greater force of
interactions. |
They are mainly found in gas form.
Some non-polar compounds can be found in liquid form. They are soft in nature. |
Melting Point |
They have higher melting points
than non-polar covalent bonds. |
They have a very low melting point
because they don’t have any polarity. |
Boiling Point |
They
have a higher boiling point than non-polar covalent compounds. |
They have a very low boiling point. |
Conductivity |
They
conduct electricity while they are in the solution state. It is due to the
mobility of ions. |
They don’t conduct electricity as
they are insulators |
Solubility |
They
are highly soluble in polar solvents like water. |
They are less soluble in water but
are soluble in nonpolar solvents like CCL4, CHCL3, etc. |
Polar Molecules
- They orient themselves in the presence of an electric field with a positive end of the molecule, that is attracted to the negative plate. While the negative end of the molecule is attracted to the positive plate.
- They can have polar covalent bonds or ionic bonds.
- Polar molecules affect the properties of polar compounds like water. They tend to stick together and line up in groups.
Examples of Polar Molecules
- Hydrofluoric Acid (HF)
- Water (H2O)
- Acetone
- Sulphur dioxide (SO2)
- Ammonia (NH3)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Ethanol (C2H5OH)
- Methanol (CH3OH)
- Hydrogen Sulphide (H2S)
- Chloromethane (CH3Cl)
- Ozone (O3)
- Phosphorus trichloride (PCL3)
Non-Polar Molecules
- Charges in non-polar molecules are equally distributed across molecules.
- They are generally symmetrical, like tetrahedral molecules.
- They are insoluble in water but dissolve in nonpolar solvents.
- Carbon dioxide (Co2)
- Hydrochloric acid (HCL)
- Benzene (C6H6)
- Methane (CH4)
- Carbon tetrachloride (CCL4)
- Boron trifluoride (BF3)
- Hexane (C6H14)
- Nitrogen (N2)
