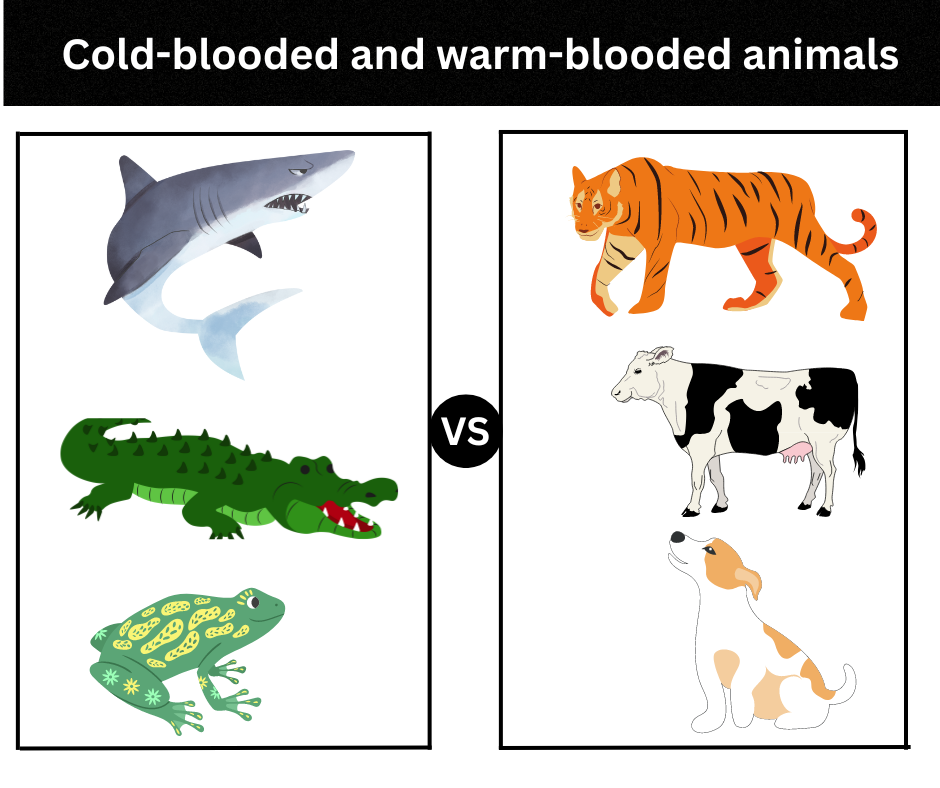
On the basis of regulating internal body temperature, there are two types of animals, that are Cold blooded animals and warm blooded animals. In simple language, animals that cannot regulate their internal body temperature according to the external environment’s temperature are known as cold blooded animals. While Animals that can maintain their internal body temperature irrespective of the environment’s temperature are known as warm blooded animals.
 |
| Cold blooded and Warm blooded animals |
Cold blooded animals definition
- The body temperature of cold blooded animals is keep changing as they move to different habitats due to changes in external temperature.
- They cannot survive in extreme temperatures as their body temperature is not constant and keeps changing.
- They can survive on very less amount of food as they do not need much energy to survive.
- They are much more resistant to the disease and use their body temperature as a defense mechanism against diseases.
- They lower their body temperature if they got any diseases which helps them to recover.
- They have two phases i.e. Hibernation and Aestivation.
- In winter, they rest in warm places. The winter resting period is known as Hibernation.
- In summer, they rest in cool and shady places. The summer resting period is called Aestivation.
- Examples of cold blooded animals are fish, reptiles, frogs, crocodiles, amphibians, bees, moths, and termites.
- There are three types of cold blooded animals: ectothermy, poikilothermy, and bradymetabolism.
- Ectothermy- Cold blooded animals of this group maintain their body temperature according to the external environment’s temperature. Example- Reptiles.
- Poikilothermy- The body temperature of cold blooded animals of this group fluctuates with the change in temperature of the surrounding. Example- Frogs and turtles.
- Bradymetabolism- Cold blooded animals of this group maintain their temperature according to the rate of metabolism. Example- Insects.
Warm blooded animals definition
- The body temperature of these animals remains constant throughout their life i.e. in the range of 35 to 40 degree Celsius.
- Mitochondria of warm blooded animals produce heat energy which is utilized to maintain the internal body temperature.
- These animals are also known as homeothermic animals and use thermal homeostasis to maintain their body temperature.
- They have a strong immune system to fight against diseases and a high metabolism rate.
- These animals are active in both winter and summer or warm and cold.
- Examples of warm blooded animals are Birds and Mammals.
- There are three types of warm blooded animals: endothermy, homeothermy, and tachymetabolism.
- Endothermy- Warm blooded animals of this group maintain their body temperature by the use of internal means like sweating, shivering, etc. For example a dog.
- Homeothermy- The animal’s body of this group regulates its internal temperature irrespective of the external temperature. For example humans.
- Tachymetabolism: These warm blooded animals use a high metabolism rate to maintain their body temperature. For example birds.
Major Differences (Cold blooded vs warm blooded animals )
|
Basic for comparison |
Cold blooded animals |
Warm blooded animals |
|
Definition |
Animals that cannot regulate their internal body temperature |
Animals that |
|
Also Known |
Poikilothermic |
Homeothermic |
|
Types |
Cold blooded
Ectothermy |
Warm blooded
Endothermy |
|
Temperature |
Cold blooded animals are dependent on the external environment’s temperature. |
Warm blooded |
|
Metabolic |
Cold blooded animals’ metabolic rate changes according to the environment. |
Warm blooded |
|
Phase |
They |
Most of |
|
Organ |
They do not |
They have |
|
Heat |
They |
They |
|
Resistance |
They use |
Warm blooded |
|
Energy |
They gain |
They produce |
|
Survival |
They cannot |
They can quickly |
|
Heat |
Cold blooded |
They can |
|
Proteins |
They have |
Proteins in |
|
Genome |
Their |
Their |
|
Effects |
Excessive body fat can overheat their body temperature and can cause death. |
Body fat is |
|
Examples |
Examples of |
Examples of |
Examples of Cold blooded animals